First, what is NFPA 652 and why is it important? How does it impact our handling of fire and explosion safety concerns and regulations? Where and why did NFPA 652 originate?

Let’s go back a bit further. The National Fire Protection Association or NFPA is a nonprofit organization that creates health and safety standards to protect against a variety of fire hazards. Each year they develop and review standards and codes which are or have been adopted by municipalities and corporations, etc. If adopted, we need to adhere to them.
In the industrial ventilation sector, there are several major codes we encounter and frequently implement, including:
- NFPA 654: Standard for the Prevention of Fire and Dust Explosions from the Manufacturing, Processing, and Handling of Combustible Particulate Solids
- NFPA 68: Standard on Explosion Protection by Deflagration Venting
- NFPA 484: Standard for Combustible Metals
- NFPA 69: Standard on Explosion Prevention Systems
- NFPA 61: Standard for the Prevention of Fires and Dust Explosions in Agricultural and Food Processing Facilities
- NFPA 664: Standard for the Prevention of Fires and Explosions in Wood Processing and Woodworking Facilities
And now we have NFPA 652, “Standard on the Fundamentals of Combustible Dust.”
NFPA 652 was developed to encompass the other relevant NFPA codes regarding explosion and combustible dust and bring them all together. Those codes that had compatibility issues were to be corrected with 652.
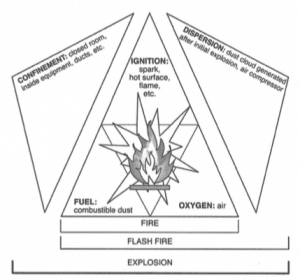
Diagram shows the requirements for a fire, flash fire and an explosion.
The significance of combustible dust in the industrial ventilation sectors is major. Past events and the investigations completed by the Chemical Safety Board (CSB) have clearly shown the catastrophic effects of combustible dust explosions on employee safety, capital equipment, and building structures. When an ignition source, combustible dust or fuel, containment, oxygen, and dispersion are present and in proper concentrations, an explosion could occur.
After saying all that, if you’re aware of and adherent to the previously posted NFPA Standards, what are the significant points of 652? What does it mean to you?
The Significant Points Presented by 652 are:
- Chapter 7 of NFPA 652 requires all facilities to have a Dust Hazard Analysis or DHA performed within three years from the issue of the Code or completed by September 2018. Exceptions are the agricultural and food processing industries covered by NFPA 61 and the wood processing industry covered by NFPA 664 which are proposing to extend the DHA requirement to 5 years or September 2020. A DHA, in regards to this standard, is “A careful review of the fire, deflagration and explosion hazards to determine the consequences of what could go wrong and to determine what safe guards could be implemented to prevent or mitigate those consequences.”
- Chapter 5 allows for historical facility data to be deemed representative of current materials and process conditions. This is critical for new processes that do not have dust to test. It gives the manufacturer a starting point from which to base their initial design and then test the actual dust once they are in production.
- NFPA 652 has allowed the industry related standards to prevail when in conflict and is becoming the minimum standard through subcommittees. When 652 is not detailed enough, other standards more specific to the industry are used, such as NFPA 61 which addresses the prevention of fires and dust explosions in the agricultural and food processing industries. NFPA 61 is much more detailed as it is tailored only to food related processing and will give more direction than other general standards such as 654 and 652.
That’s it. Now you know what needs to be completed. Need help or have additional questions. Call us!


